
Get to Know
Shafi Goldwasser
Discover why we turned Shafi into a superhero
WHO IS SHAFI GOLDWASSER?
Name: Shafi Goldwasser
Born: 1958
Occupation: Computer Scientist
Nationality: Israeli
Shafi is an Israeli-American computer scientist best known for her work in cryptography. She was born in 1958 in New York City and moved with her family to Israel at the age of six, where she attended school in Tel Aviv. Shafi completed her undergraduate degree in mathematics at Carnegie Mellon University and later earned her Ph.D. in computer science from Berkeley.
She co-invented probabilistic encryption—a method that makes it nearly impossible to decode encrypted messages without a key. Along with Silvio Micali, she developed the foundations of zero-knowledge proofs, which allow one party to prove to another that something is true without revealing any additional information. Their work has had lasting impact in securing digital communications and online privacy. To find out more in this video.
Born: 1958
Occupation: Computer Scientist
Nationality: Israeli
Shafi is an Israeli-American computer scientist best known for her work in cryptography. She was born in 1958 in New York City and moved with her family to Israel at the age of six, where she attended school in Tel Aviv. Shafi completed her undergraduate degree in mathematics at Carnegie Mellon University and later earned her Ph.D. in computer science from Berkeley.
She co-invented probabilistic encryption—a method that makes it nearly impossible to decode encrypted messages without a key. Along with Silvio Micali, she developed the foundations of zero-knowledge proofs, which allow one party to prove to another that something is true without revealing any additional information. Their work has had lasting impact in securing digital communications and online privacy. To find out more in this video.

In The Remarkablz Universe, Shafi can wrap any information in a riddle that is impossible to solve. Shafi always exhibited a genius level intellect but dreamed of becoming an improv actress. A twist of fate that should have left her dead instead found putting her computer science abilities and knowledge of technology to use. Shafi now wraps Team Remarkablz messages into coded riddles that their enemies are unable to solve.
Superhero Backstory
Shafi features in our signature card game, Top Quarkz. The game supports the development of maths, literacy and decision-making skills all while learning about some of the most impressive scientific discoveries throughout history. She also features in our colouring poster, Fetters Chaos
We've explained the drawing and her playing card below so you can learn more.
We've explained the drawing and her playing card below so you can learn more.
Shafi can wrap any information in a riddle that is impossible to solve.
- The background of this drawing is the Weizmann Institute of Science. Shafi became a professor at the Weizmann Institute of Science in 1993.
- Probabilistic encryption is the use of randomness in an encryption algorithm, so that when encrypting the same message several times it will yield different ciphertexts.
Superpower
Shafi is the co-inventor of probabilistic encryption.
The Blum-Goldwasser (BG) cryptosystem was co-created by Shafi.
Location
SideKick
Shafi's PhD supervisor was Manuel Blum.
A side channel attack breaks cryptography.
Weakness
Each drawing we create has one or more hidden treasure(s) about our superheroes' life experiences, depictions in art, jobs or discoveries. Did you find the ones hidden in this drawing?
Discovery
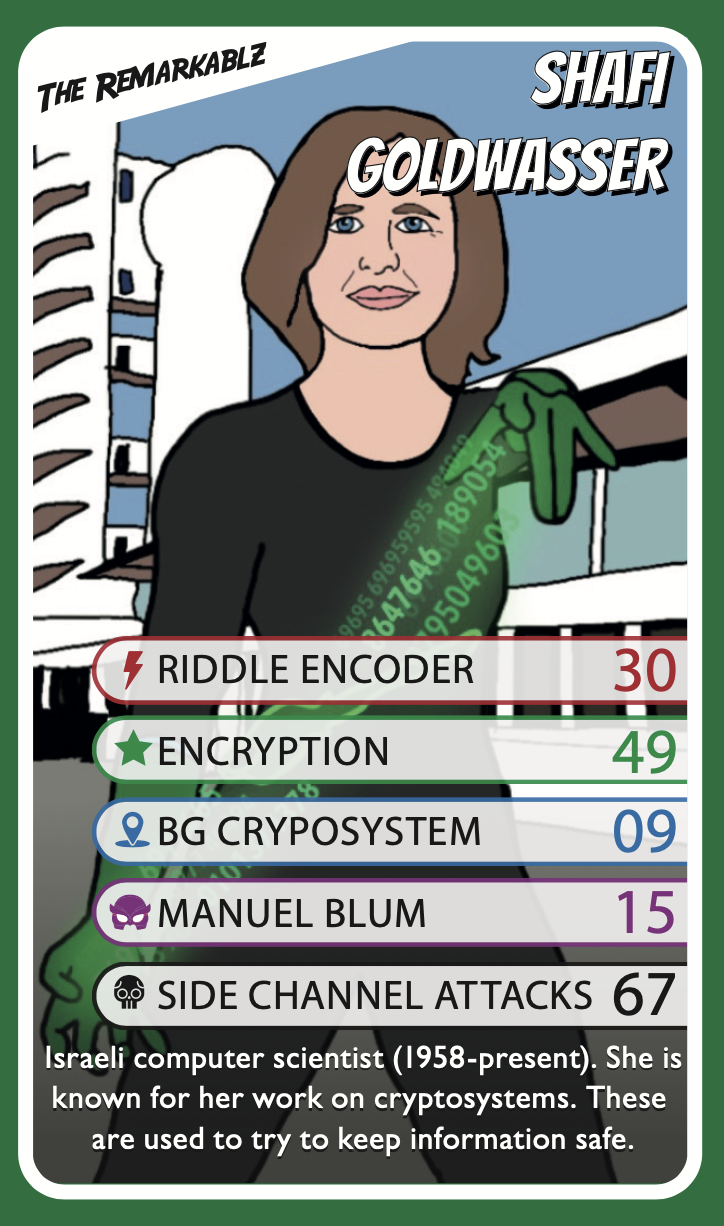
We have packed a lot into our Top Quarkz playing cards - from amazing imagined superpowers to biographical information and hidden treasures.
What do Computer Scientists do?
Computer scientists design new software, solve computing problems and develop different ways to use technology. Computer scientists need to look at a problem and work out a way a computer might be able to help solve it. This is called computational thinking. You don't realise it but you use computational thinking every day. Anytime you analyse a problem and plan out the solutions, you are using computational thinking. Video credit: McGrawHill
Cryptography is a way of keeping information secret by turning it into code. It helps protect messages so that only the right person can read them. This is called encryption. To unlock the message, you need a special key to change the code back into words. Cryptography is used to keep things like passwords, text messages, and websites safe from hackers. Find out more with this video from SciShow.
Encryption is a way of hiding information so that only certain people can read it. It turns a regular message into secret code. To read the message, you need a special key to unlock or decrypt it. Mia Epner, who works on security for a US national intelligence agency, explains how cryptography allows for the secure transfer of data online. Video credit Khan Academy
- cryptography comes from greek "Kryptos" and "Graphein" meaning "Hidden word".
- Julius Caesar used encryption to cipher letters and messages. These are known as Caesar ciphers.
- In a Caesar cipher, each letter in is changed by three. A becomes D, B becomes E, and so on.
- When a message is sent using cryptography, it is changed (or encrypted) before it is sent.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography Fun Facts!
The Caesar Cipher is one of the oldest and simplest ways to hide a message. It’s named after Julius Caesar, who used it to send secret messages over 2,000 years ago. This video explains the Caesar cipher, the first popular substitution cipher, and shows how it was broken with "frequency analysis". Video credit: Khan Academy
What's the Caesar Cipher?
What is Encryption?
Ask A Scientist: 100 Big Questions from Kids Around the World!
EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES
Ask a Scientist puts the fun back into science in this thrilling book for children aged 6-9. All the popular science topics are covered, with weird and wacky questions and clear and lively answers. Find out more about Ask a Scientist- by Robert Winston
Fun Cryptography Activity: Make Your Own Caesar Cipher!
Caesar used a code that shifted the alphabet by three letters. To decode a message his generals had to shift the letters backwards three letters. The table above shows you shift. Let's give it a try.
What you will need
- Paper
- Pencil or Pen

Find another great class room activity here

VKDIL IV D VFLHQFH VXSHUKHUR
When you are ready Hover of the box below to find the answer!
Now you try, write a few sentences or send a message to a friend!
Now you try, write a few sentences or send a message to a friend!
Shafi is a science superhero
This image may be hard to see on mobile.
Learn how Julius Caesar used secret codes to protect his messages! In this easy cryptography activity for kids, you’ll decipher a Caesar Cipher.
Can you crack this secret message?
Sign up to our Newsletter
By signing up to receive emails, you agree that we may use the personal information provided by you to send you marketing emails. You can opt out of these emails any time by clicking the unsubscribe link or by contacting us. To see how we use your personal data, please see our Privacy policy.





